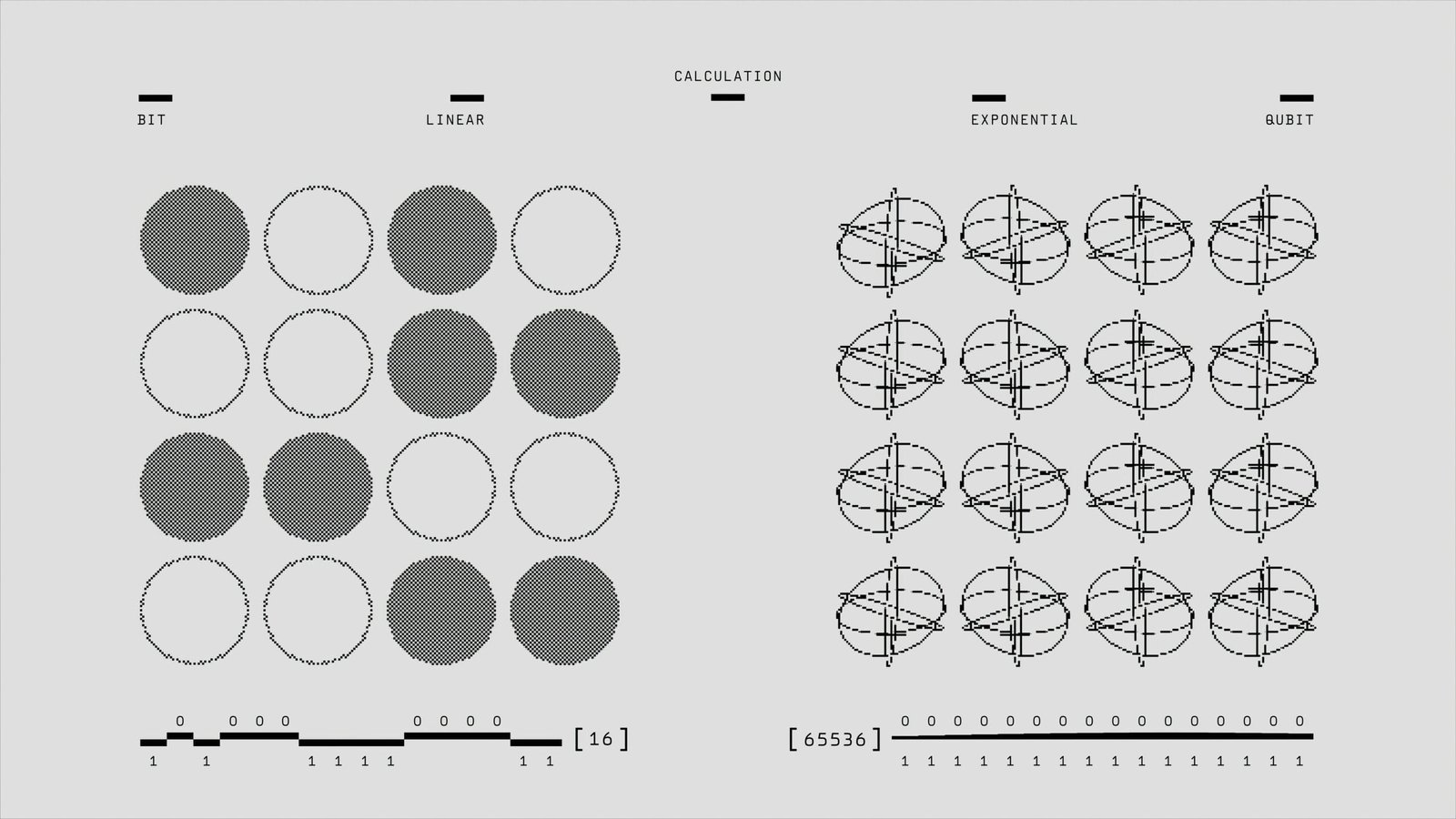
Chinese Technology Integration Comparison: 7 Shocking Differences
Most believe that the United States and Western nations dominate the global technology landscape. However, Chinese technology integration has surpassed expectations, revolutionizing industries and setting new global standards. From artificial intelligence to 5G, China is shaping the future with rapid digital transformation, outpacing competitors in key technological sectors.
So, how do China’s digital transformation and Chinese technology integration compare globally? Let’s dive deep into the facts and uncover surprising insights into China’s AI-driven automation, smart cities, fintech, and more.
The Rise of China’s Digital Transformation
Many assume that China’s tech industry is purely driven by imitation rather than innovation. But in reality, China has evolved into a global technology powerhouse, pioneering advancements in AI, automation, and digital infrastructure.
China’s Digital Transformation Strategy: Beyond Catching Up
Unlike many Western nations that gradually adopted digital transformation, China took an aggressive and strategic approach, investing billions in AI, automation, 5G, IoT, and blockchain technology. The Chinese government has actively supported this transformation through its “Made in China 2025” initiative, aiming for self-reliance and technological supremacy.
Big Data and AI are at the core of this transformation, allowing China to lead in AI-driven automation across various industries. Smart infrastructure, including intelligent transportation and energy-efficient cities, has placed China at the forefront of global digital advancements. While many countries are still rolling out 5G, China has already begun research into 6G technology development, further solidifying its position as a tech leader.
China vs. Western Nations: A Different Approach to Innovation
Western companies like Google and Apple focus on iterative innovation and ecosystem building, while China prioritizes state-backed industrial innovation and rapid market adoption. The U.S. relies on private enterprises for AI development, whereas China integrates AI into national policy, accelerating its adoption across key industries.
China’s AI-driven surveillance, for instance, is widely used for security, whereas Western countries remain cautious due to ethical concerns. Additionally, China’s AI-powered logistics and automation in supply chains far exceed Western counterparts in terms of efficiency and scalability.
AI and Big Data: The Backbone of China’s Digital Economy
The widespread adoption of AI and big data in China is no coincidence. The country has access to vast amounts of data, allowing its AI systems to train and develop at a pace unmatched by competitors.
China’s AI-driven facial recognition technology is used extensively for security, banking, and even social credit scoring. AI automation is transforming industries like logistics, where autonomous delivery robots and AI-powered warehouses streamline operations. Healthcare, too, is witnessing AI integration in diagnostics, improving accuracy and early detection rates. With the rapid rise of AI-driven automation, China is not just catching up—it is setting new global standards for digital transformation.
AI and Automation: China’s Strategy for Global Dominance
A common misconception is that China’s AI and automation are only focused on manufacturing. The truth is that China is integrating AI into nearly every aspect of life, from self-driving cars to facial recognition payment systems.
AI-Driven Automation Across Industries
China’s AI-powered automation is reshaping industries that were once heavily dependent on human labor. This shift is not just about efficiency—it’s about building a self-sufficient digital economy.
Manufacturing in China is transforming, with smart factories equipped with AI-driven automation optimizing production processes. AI-powered robotics in Chinese industries are minimizing human errors while maximizing productivity. Healthcare is also benefiting from AI integration, with AI-powered diagnostics significantly improving patient outcomes. AI-driven fintech solutions, such as blockchain-based financial transactions and fraud detection, are enhancing China’s already advanced digital economy.
Case Study: China’s AI-Driven Facial Recognition Technology
While Western nations debate the privacy risks of AI surveillance, China has fully embraced AI-driven facial recognition technology.
Beijing and Shanghai have implemented facial recognition for public security and traffic monitoring, helping authorities prevent crimes in real time. Businesses like Alibaba and Tencent leverage facial recognition for cashless transactions, allowing consumers to pay simply by scanning their faces. The technology is even making its way into education, where schools use AI-driven systems to track student engagement in classrooms. China’s AI-led surveillance ecosystem is shaping the way governments and businesses use technology for enhanced security and efficiency.
China’s 5G and 6G Revolution: Faster and Smarter Connectivity
Many assume that 5G is still in its early stages, but China has already established itself as the global leader in 5G network deployment. Not only has China outpaced competitors in 5G adoption, but it is also pioneering 6G development, setting the stage for next-generation connectivity.
How 5G in China is Outpacing Global Competitors
China leads the world in 5G infrastructure, with the largest number of 5G base stations globally. Companies like Huawei and ZTE have played a crucial role in rolling out high-speed 5G networks, enabling ultra-fast internet connectivity across major cities.
China’s digital infrastructure and smart cities benefit immensely from 5G’s low latency, which powers advancements in autonomous vehicles, AI-driven industries, and real-time IoT applications.
The Role of 6G Development in China’s Digital Infrastructure
While most countries are still adopting 5G, China is already investing in 6G research and development. 6G is expected to offer speeds up to 100 times faster than 5G, enabling innovations like holographic communication, AI-powered edge computing, and quantum networking.
With 6G, China aims to create an even more interconnected and efficient digital economy, enhancing AI-driven automation and next-gen industrial applications.
China vs. The World: Smart Cities and IoT Adoption
Most people assume that smart cities are a futuristic concept. However, China has already implemented AI-powered smart city solutions, integrating automation, IoT, and data-driven governance.
How China’s Smart Cities Use AI, Automation, and IoT
Chinese cities like Beijing and Shenzhen have adopted AI-powered traffic systems, automated waste management, and intelligent security surveillance, improving urban efficiency. IoT adoption in China allows real-time monitoring of energy usage, reducing waste, and optimizing urban infrastructure.
Comparison: Chinese vs. Western Approach to Smart Cities
Unlike Western nations that focus on privacy regulations, China prioritizes data collection and real-time AI analysis to improve city operations. The Chinese government works directly with tech giants like Alibaba, Tencent, and Huawei to deploy smart city initiatives at an unprecedented scale.
Examples: Beijing’s AI-Powered Traffic Systems and Shenzhen’s Smart Infrastructure
Beijing’s AI-driven traffic control reduces congestion using real-time data, optimizing road signals dynamically. Shenzhen, often called China’s “smart city prototype,” features 5G-powered surveillance, cashless payments, and fully automated public transport systems.
The Evolution of E-Commerce & Fintech in China
Many believe that China’s e-commerce success is solely due to its large population, but the reality is that its rapid innovation, AI integration, and blockchain technology have propelled it far ahead of many global competitors.
How Alibaba, Tencent, and JD.com Revolutionized E-Commerce
China’s e-commerce platforms are powered by AI-driven recommendation engines, smart logistics, and automated warehouses, providing a seamless shopping experience. Unlike Western platforms like Amazon, Chinese e-commerce is deeply integrated with social media, allowing users to shop directly through platforms like WeChat and Douyin (China’s TikTok).
AI chatbots and automated customer support handle millions of queries daily, improving efficiency and user experience. Additionally, China’s investment in drone deliveries and autonomous logistics ensures rapid, cost-effective shipping across urban and rural areas.
Blockchain Technology Adoption in China’s Finance Sector
China’s fintech ecosystem is built on blockchain security and decentralized finance (DeFi). Digital yuan vs cryptocurrencies is a key debate, with China’s government pushing its centralized digital currency electronic payment (DCEP) system to replace cash transactions while restricting decentralized cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin.
While the West relies on traditional banking, China has leapfrogged into a cashless economy, where mobile payments dominate. Alipay and WeChat Pay facilitate instant transactions, eliminating the need for credit cards. China’s financial ecosystem integrates AI-powered fraud detection and blockchain-based transactions to enhance security and efficiency.
China’s Semiconductor and Chip Manufacturing Race
Many assume that China relies entirely on Western semiconductors, but recent developments have shown that China is aggressively pushing for self-sufficiency in semiconductor manufacturing.
The Struggle for Semiconductor Self-Reliance Due to US Sanctions
U.S. sanctions on Chinese tech companies like Huawei have accelerated China’s focus on domestic chip production. China is investing heavily in semiconductor R&D to reduce its dependence on Western chip manufacturers like Intel and Qualcomm. China’s semiconductor industry is now developing advanced 7nm and 5nm chip technology, aiming to compete with industry leaders like TSMC and Samsung.
The Rise of Chinese Chip Manufacturing and Its Global Implications
Companies like SMIC (Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corporation) are spearheading Chinese chip manufacturing, with government backing to expand production capabilities. China vs US technology race is intensifying, affecting global supply chains and reshaping geopolitical alliances in the tech industry.
With increasing investment in AI chips, quantum computing, and photonic processors, China is not just catching up—it’s working to dominate the future of semiconductor innovation.
Cybersecurity and Privacy Concerns in China’s Digital Growth
Many assume that China’s rapid technological advancements come without significant risks. However, China’s cybersecurity laws and AI-driven surveillance technology have sparked global debates on privacy and data protection.
How China’s Cybersecurity Laws Affect Global Businesses
China’s Cybersecurity Law of 2017 and subsequent regulations require foreign businesses operating in China to store data locally, comply with strict cybersecurity measures, and sometimes grant the government access to sensitive information. This raises concerns about cybersecurity risks in China’s tech integration, particularly for global enterprises that rely on cloud computing and digital infrastructure.
Global companies must navigate complex Chinese data privacy policies, which contrast with Western data protection laws like the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation). While Western policies prioritize user consent and transparency, China’s approach leans towards government oversight and national security.
Privacy Debates Around China’s AI-Driven Surveillance and Facial Recognition Tech
China is home to some of the most advanced AI-driven surveillance technology, with cities like Beijing and Shenzhen implementing facial recognition for security, public safety, and even payment verification. This level of integration has sparked concerns about data privacy in China and its implications for civil liberties.
Unlike in Western countries, where privacy advocates push back against mass surveillance, China embraces state-controlled AI technology to enhance law enforcement and social governance. The debate continues whether this AI-driven surveillance technology is an innovation for security or a privacy invasion.
Comparison: China vs. Western Data Privacy Policies
The fundamental difference between China and the West lies in the approach to data privacy governance.
- China’s data privacy policies focus on government oversight, with technology used as a means of state control.
- Western data privacy policies, such as GDPR, emphasize consumer rights and data transparency, often limiting how companies and governments can collect and use data.
As China continues integrating AI, IoT, and 5G into everyday life, questions remain about how these technologies will impact global privacy norms and cybersecurity strategies.
The Future of Chinese Technology Integration: What’s Next?
A common belief is that China has reached its peak in technological innovation. However, emerging technologies like quantum computing, metaverse development, and Chinese green technology integration prove that China is just getting started.
Predictions for China’s Edge Computing Innovations, Metaverse Development, and Quantum Computing
China is making aggressive strides in edge computing to enhance AI capabilities and real-time data processing. With companies like Alibaba Cloud and Huawei leading metaverse development in China, we can expect more integration of virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and blockchain-based digital ecosystems.
Quantum computing in China is also progressing rapidly. The country’s investment in quantum encryption and next-gen computing infrastructure could give it a major advantage in cybersecurity and AI advancements.
The Role of Chinese Technology Integration and Smart Factories
China is not only focusing on digital transformation but also on Chinese technology adoption. Smart factories in China are utilizing AI and IoT to reduce energy consumption and optimize industrial production.
China’s focus on renewable energy and carbon neutrality aligns with its ambition to lead the world in sustainable technology development. The integration of green tech with AI-driven automation is setting new standards for eco-friendly industrialization.
What the World Can Learn from Chinese Technology Integration Strategy
Chinese technology integration strategy offers key takeaways for global policymakers and businesses:
- Government-backed innovation accelerates growth – Policies such as “Made in China 2025” demonstrate the impact of long-term national tech strategies.
- Mass adoption of digital finance and e-commerce – China’s cashless society model shows how fintech can transform traditional economies.
- AI-driven automation enhances efficiency – From smart cities to logistics, China’s AI-first approach is redefining global industries.
Conclusion: Is China Truly Leading the Global Tech Race?
China’s technological advancements in AI, 5G, IoT, fintech, and cybersecurity have placed it at the forefront of the global digital transformation. While Western nations focus on regulatory measures and consumer privacy, China is rapidly deploying large-scale tech infrastructure to fuel economic growth and national security.
However, China’s innovation trends face challenges – geopolitical tensions, semiconductor dependencies, and privacy concerns may impact its long-term dominance. The battle for technological supremacy is far from over, and global competition will continue to shape the future of innovation.